July is UV Safety Month - click here for FREE healthy vision tips
Menu
“Within 6 months 93% of patients had arrested or improved their ARMD condition, (both wet and dry). The improvements continued until the trial ended at 24 months.”
Effects of melatonin in age-related macular degeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Dec;1057:384-92.. Yi C, Pan X, Yan H, Guo M, Pierpaoli W. Department of Fundus Diseases, Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, Sun Yat-Sen University, 510060 Guangzhou, China: Pubmed: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16399908
The study included 55 to 100 patients with both wet and dry macular degeneration for a period of 6 months, with two years of follow up exams. The participants were given a, patented, formulation, now called, ARMeD™ to learn if a healing response was possible.
Dr. Changxian Yi stated; “Our purpose was to explore a new approach to prevent and/or treat ARMD.” The study was also monitored by, world renowned endocrine specialist and melatonin expert, Dr. Walter Pierpaoli.
In the beginning, Dr. Changxian Yi’s theory was that a specific combination of melatonin, selenium and zinc would have the capacity to control eye pigmentation and thereby regulate the amount of light reaching the photoreceptors in the eye. The unique nutrient combination in the tablets would also scavenge hydroxyradicals and help to protect retinal pigment epithelium cells from oxidative/free radical damage which is considered to be a precursor to ARMD.
The patients were then evaluated at regular periods and the initial results were dramatic, at 2-3 months of treatment the visual acuity had been stabilized, no further degeneration had occurred. A significant step toward helping those who suffer with this disease, but that was just the beginning…
At the end of the study the vast majority had dramatically reduced pathologic macular changes. Additionally the patients reported better vision with improvements to glare, dryness, clarity and comfort.
For the trial participants, who continued past 6 months onto 12-months of nightly use, the changes in their fundus pictures were remarkable, (please note the before and after eye pictures presented within this article in figures 1-3).
Figure 1
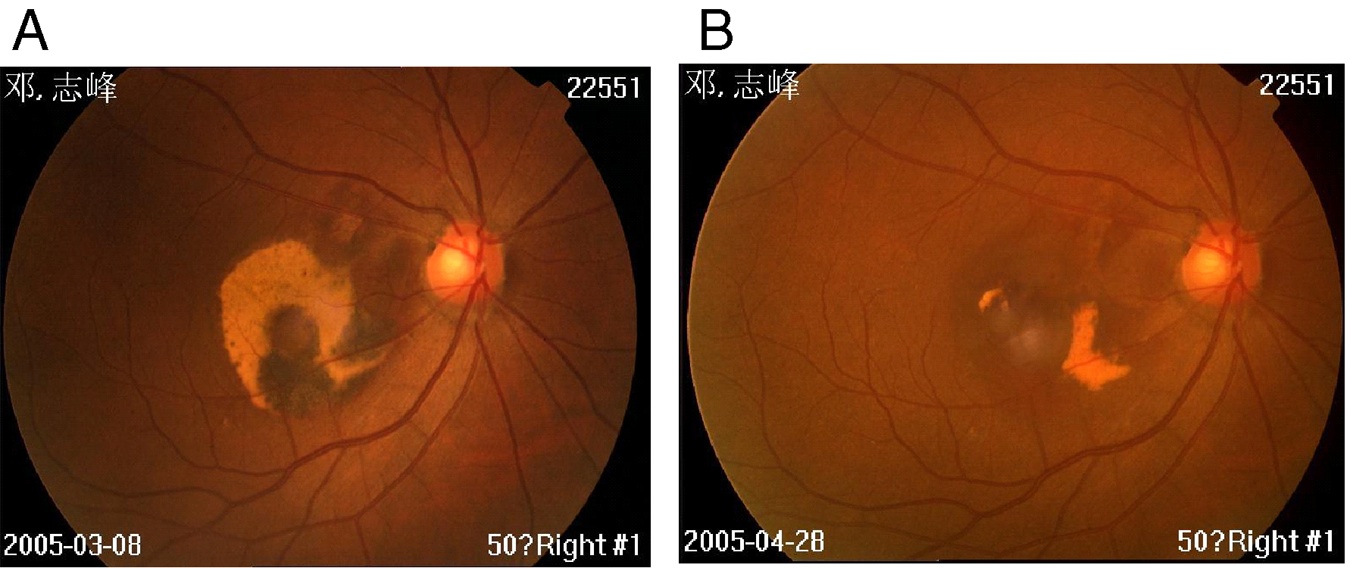
Figure 1: The left slide shows the eye of a 67 year old male before treatment, his vision has been deteriorating for 2 years. The right picture shows the same eye 2 months later after ingestion of one tablet every night at bed time. He now has stable visual acuity of 0.3 with remarkable improvements in sub-retinal macular hemorrhage. In this study of 100 patients, 90% had, to varying degrees, regressed or reversed their ARMD within the first 6 monthsSource: Changxian Yi et al, effects of melatonin in age-related macular degeneration, Ann NY Acad Sci, 1057:384-392,2005
Figure 2
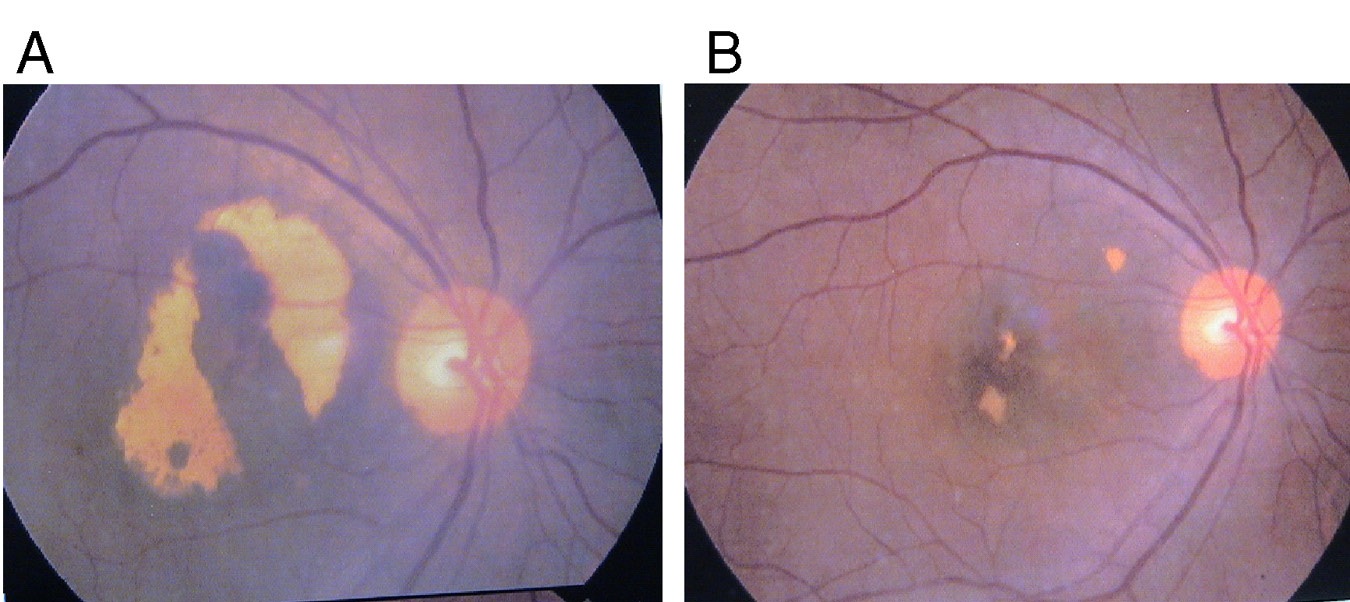
Figure 2: The left slide shows the eye of a 71-year old female with ARMD who after 6-months had her vision improve from 0.2 to 0.4 (as indicated in the right slide).
Figure 3
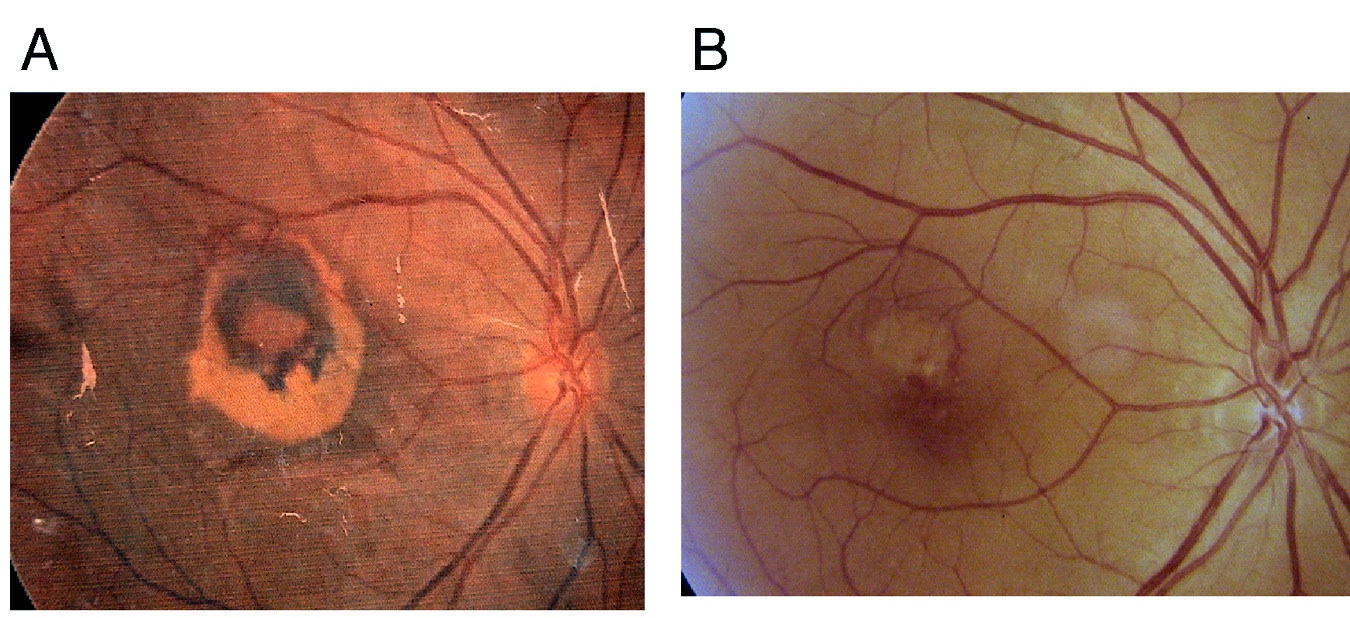
Figure 3: A 58 year old male whose visual acuity at the start (left slide) was 0.2. This improved to 0.4 after 6-months of regular use. The sub-retinal hemorrhage and exudates was remarkably absorbed.
The study authors stated “Melatonin has been shown to have the capacity to control eye pigmentation and thereby regulate the amount of light reaching the photoreceptors, to scavenge hydroxyradicals and to protect retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells from oxidative damage. Therefore, it is reasonable to think that the physiological decrease of melatonin in aged people may be an important factor in RPE dysfunction”
Eye pigmentation regulates the amount of UV light reaching the photoreceptors of the eyes. The macular pigment contributes to the protection of the retinal cells from free radicals caused by stress and the sun’s UV radiation.
Melatonin provides powerful antioxidant protection for the tissues of the eyes, safeguarding the retinal epithelium (RPE) from oxidative damage. Clinical studies have shown that it may have a promising role in the safe treatment and management of Glaucoma.
Melatonin improves the body’s natural and optimal night-peak release of Melatonin. This bonded melatonin formula, when taken nightly, was found to re-establish optimal circadian rhythms, resulting in healing and repair response in the eyes.
According to clinical studies, Melatonin, being an efficient antioxidant with antinitridergic properties, has a promising role in the treatment and management of glaucoma. These same potent antioxidant properties could also protect the tissues of the eye against Age-Related Macular Degeneration, Cataracts, Glaucoma and other disorders.(1)
Zinc is vital to keeping your eyes healthy and vision sharp. Zinc is concentrated in a part of the retina called the “macula” and helps Vitamin A produce melanin, a pigment which has a protective effect on the eye. A deficiency in zinc has been associated with reduced night vision, while supplementation with zinc has been shown to slow the rate of age-related macular degeneration due to its importance in maintaining a healthy macula.(1) Zinc has also been shown to reduce cataracts by as much as 36% in people ages 65-74.(2)
Research has shown that zinc can correct age-related immuno-depression and several other hormonal and metabolic changes. It has been found that the low zinc levels in aging animals can be restored to normal values with either nocturnal administration of melatonin or transplantation of the pineal gland from young into older animals. Zinc is an essential component of more than 200 enzymes and one of the most relevant trace elements in the body. It is thus clear that additional zinc must be supplemented daily, in order that melatonin can better exert its anti-aging activities on the entire hormonal and immune systems! This important and novel scientific observation of the powerful anti-aging and immuno-enhancing activity of the combination of zinc and melatonin has contributed to the development of ARMeD™ which was proven effective in the clinical trials.
Selenium is essential for the enzymatic reaction responsible for the synthesis of glutathione, a powerful physiological molecule which constantly protects the body from oxidative damage. A lack of selenium will thus result in a loss of the detoxification capacity of the body, immuno-depression and onset of degenerative diseases such as cancer.
Selenium, a mineral and antioxidant found naturally in foods like Brazil nuts, can reduce the risk of developing macular degeneration and act as a strong antioxidant for eye protection.(1) Selenium, when combined with Melatonin, also may help decrease levels of toxic MDA while significantly increasing levels of the powerful antioxidant Glutathione.(2)

When asked about this recent finding, Dr. Pierpaoli stated; “Many people are aware of melatonin’s role in jet-lag, or as a potent antioxidant. Our research with this particular synergistic combination has highlighted its ability to re-synchronize the endocrine system as well as circadian rhythms of the wake-sleep cycles.
I note that while much has been discussed about the amazing ability of melatonin to, control eye pigmentation, regulate the amount of light reaching the photoreceptors and other functions in relation to eye structure; I surmise that the rebalancing of hormones and improvement of repair functions through the improved circadian sleep cycles are equally significant factors pointing to this formula’s ability to favorably impact both wet and dry age related macular degeneration as well as Glaucoma.”
Dr. Pierpaoli went on to say; “We’ve seen many miraculous reversals of diseases in our patients with this formula. This latest study showing that it can even reverse age-related macular degeneration is truly a breakthrough in treating this condition.”
Asked whether there may be further studies targeting ARMD and melatonin, Dr. Pierpaoli said; “We accept that additional studies are needed to further confirm these results, however we are delighted that a vital benefit to slow, halt and even reverse ARMD has been discovered. Whatever the outcome of further research into these pathways and actions, the fact remains that thousands, even millions of people can now benefit from this research to protect their vision.”
References:
Free shipping on all US orders
Your data is safe
Satisfaction guaranteed
Email support is always available

*Disclaimer: The above statements have not been evaluated by the FDA. They are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease or condition.
If you have a health condition or concern, consult a physician or your alternative health care provider.
Always consult a medical doctor before modifying your diet, using any new product, drug, supplement, or doing new exercises.
Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our Shipping and Returns Policy, our Terms and Conditions and our Privacy & Cookies Policy
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Any questions? We’re here to help.